Introduction to Psychology
It is much more than a subject.it is the scientific mirror of human behaviour and mental processes.The word “Psychology” is derived from two Greek terms.
- Psyche meaning soul or science,
- Logos meaning study or science
Thus,the original meaning of “the study of the soul.”
The first documented use of the term “Psychological” appeared in 1590 in the writings of Rudolf Goclenius, a German Scholar. However, remained a part of philosophy until 16th century, when Aristotle separated it as an independent area of study earning him the title “Father of Psychology.”

- Psyche meaning soul or science,
- Logos meaning study or science
Thus,the original meaning of psychology was “the study of the soul.”
The first documented use of the term “Psychological” appeared in 1590 in the writings of Rudolf Goclenius, a German Scholar. However, psychology remained a part of philosophy until 16th century, when Aristotle separated it as an independent area of study earning him the title “Father of Psychology.”
Meaning and Origin of Psychology
Term Meaning
Psyche Soul / Mind
Logos Study / Science
Psychology = The Science of the Soul
Historical Definitions
Definition has changed significantly through the centuries. Scholars have categorized this evolution into four key stages.
1. The Science of the Soul
Philosophers – Plato, Socrates, Descartes and Aristotle
They believed all behaviour was controlled by the soul.
According to them :-
- Soul governs human actions and emotions
- Study of the soul
- Dominant view until the end of the 16th century
Limitation:-
➥ The Soul cannot be seen or measured, making it unscientific.
2. The Science of the Mind
Thinkers – Pestalozzi, Pomponazzi
In the 17th – 18th centuries, scholars shifted the focus from soul to mind or brain.
- Human behaviour is governed by mental processes
- Study of the brain and thoughts
➥There were no proper tools to observe or measure brain activity.
3. Psychology as the Science of Consciousness
Pioneers – Wilhelm wundt,William James,Titchener
In the 19th century,the experimental method brought a new focus on consciousness.
- Study of conscious experiences
- Used Introspection as a method
Criticism :-
➥ Introspection was subjective and non-replicable.
4. The Science of Behaviour
Key figure – J.B. Watson, McDougall, Wood worth
In the early 20th century, psychology was redefined as the Science of observation behaviour.
- Focused only on measurable, visible behaviour
- Rejected Introspection and unconscious elements
J.B. Watson is called the Father of Behaviorism.
McDougall criticized consciousness based definitions in his book ‘Outline Psychology.
Major Definitions - By leading Psychologist
It has gone through many changes in its definition over time. Different psychologist have defined it according to their theories and perspectives. Let’s look at the major definitions provided by key figures in the field of Psychology.
1. Woodworth’s Definition :-
Woodworth’s defined as:
‘The Scientific study of Individual’ s activities in relation to the environment.’
This definition emphasizes the individual’s interaction with their surroundings. Woodworth believed that should focus on what a person does and how those actions are influenced by environment factors.
2. Watson’s Definition:-
John B. Watson, the founder of Behaviorism, stated.
“Psychology is the pure science of behavior.”
He rejected the study of consciousness and mental processes because they could not be directly observed. Watson’s focus was entirely on observable actions. His approach gave birth to behaviorism, where only measurable behavior is studied scientifically.
3. Skinner’s Definition:-
B.F. Skinner, a leading behaviorist, expanded Watson’s ideas. He defined as:
“The science of behavior and experience.”
According to Skinner, both behavior and the experiences behind it are important. He believed that should focus on observable behavior but should not ignore internal states completely. He used experimental methods to study learning and reinforcement.
4. Wilhelm Wundt’s Definition:-
Wilhelm Wundt, known as the “Father of Modern Psychology,” gave a different perspective. He said:
“Psychology is the science of internal experiences.”
He used the method of introspection to study consciousness. Wundt’s lab in Leipzig, Germany, was the first psychological laboratory, where he tried to make a scientific discipline by studying sensations, thoughts, and feelings systematically.
5. McDougall’s Definition:-
William McDougall defined as:
“The science of purposive or goal-oriented behavior.”
He emphasized instincts and internal motives. According to him, human behavior is driven by inner desires and purposes. He gave more importance to the practical and purposeful nature of human actions, making his approach unique among early psychologists.

Modern Definition of Psychology
“It is the scientific study of Behaviour and mental processes in both humans and animals.”
This includes both:-
- Overt Behaviour (e.g., crying, walking, laughing)
- Covert Behaviour (e.g., thinking, decision – making, dreaming)
Why is Psychology Considered a Science
Psychology uses the scientific method like other natural sciences.
- Observation
- Hypothesis formulation
- Experimentation
- Analysis
- Conclusion
It brings precision and objectivity to the study of complex human behaviour.
Core Components of Psychology
1. Behaviour
➥Actions that can be observed or measured.
- Expressed Behaviour – Talking, Running, Smilling
- Unexpressed Behaviour – Daydreaming, Planning, Internal dialogue
2. Mental Processes
➥ Internal cognitive activities like.
- Thinking
- Feeling
- Reasoning
- Remembering
- Emotional reactions
Applications of Psychology
It is widely used in various fields:
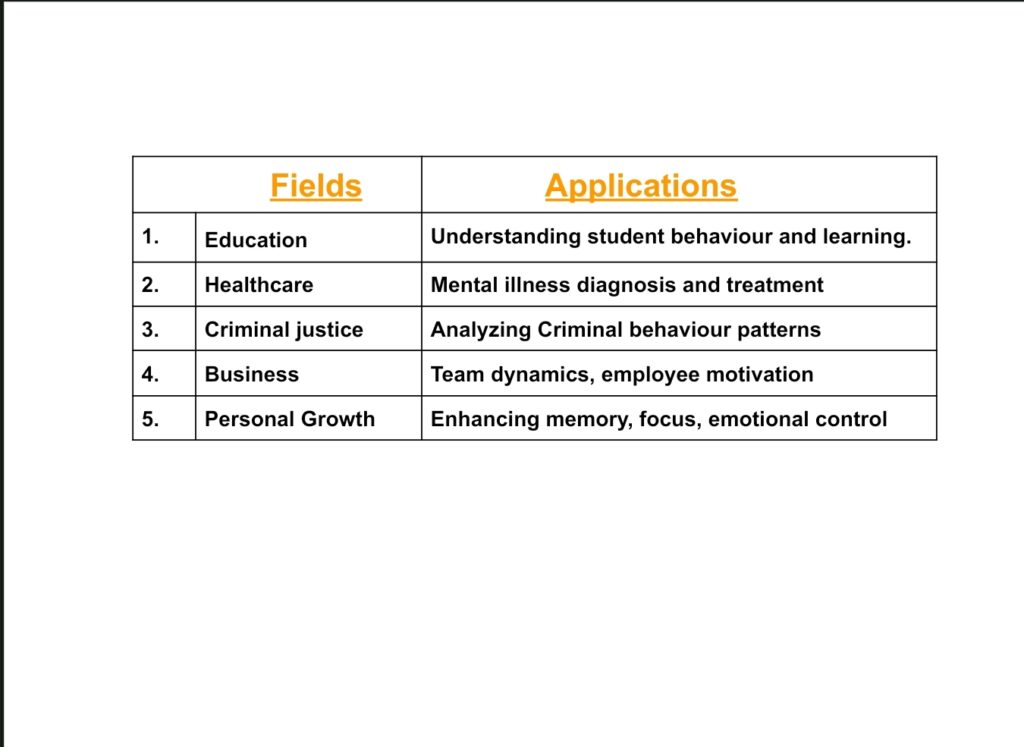
Importance of Studying
Studying helps you:
- Understand human thoughts and behaviour
- Improve interpersonal communication
- Handle stress and emotions more effectively
- Promote better mental well – being
- Build better relationships
It has evolved from abstract ideas about the soul to a precise and scientific discipline. Whether you are a student, a teacher, or a lifelong learner, understanding psychology opens the door to understanding yourself and others.
‘Psychology is not just a subject it is the mirror of human thought and behaviour.’
- You might be interested in reading this post as well:
- दादी की कहानी, Netflix से हार गया।

Pingback: Learning in psychology : Basic, Types , Explained